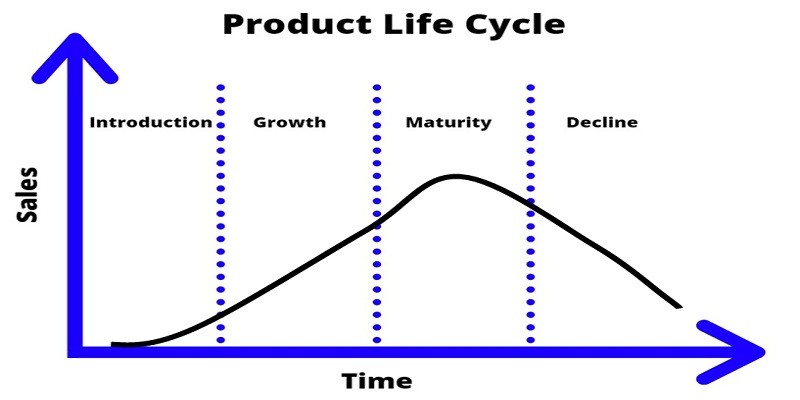
The world is built and developed with products and services. Just like humans and any other living being on earth, products also have their product life cycle. The product life cycle is the lifetime of the product in the market.
Having a piece of proper knowledge about the product life cycle is very important for business organizations. The managers can use the knowledge in the product life cycle as a tool to make strategic management decisions and to make necessary changes to the production process. It helps the managers to make necessary changes in the production process as well as pricing techniques and the competition techniques. The product life cycle was developed in 1966 by an economist named Raymond Vernon.
The life of a product begins with a simple idea and the determination to improve the idea into a real product. From the idea to the outcome, the product goes through a long journey with many developments and researches to provide the best outcome to the market. Once the final product is out in the market, the life cycle of the product begins.
There are four main stages in the product life cycle.
01. Introduction stage
This is the first stage of the product life cycle where the product is initially introduced to the market. The organization is trying to create market awareness and especially to create awareness in their target market. The organization has to concentrate on the marketing mix as the Product, Price, Place, and promotion are very important in creating brand awareness in the target market.
The customers get to know about the product for the first time. The organization needs to create a positive impression on the customers as repeat customers are one of the major assets for a growing product.
02. Growth Stage
This is the stage where brand awareness is increasing and the customers are slowly increasing the purchasing of the product. The sales and the revenue goes up and the demand for the product is continuously increasing. The organization seeks to create brand stability in the market. The brand can face pressure from the competitors in this stage and it is learning to face the competition and trying to increase the market share.
Price and product quality is well maintained to attract customers and to create customer loyalty through repeat customers. The organization conducts broader promotional methods aiming to expand the market share for the product.
03. Maturity Stage
At this stage, the rapid growth of the demand slows down but the product still has a demand in the market. The growth of the market share is less and it has reached the maximum possible production stage. At this level, the product feels the competitor pressure more and it forces the organization to emphasize the competitive advantage of the product to protect the market share. The organization is more concerned about creating price differences such as discounts, incentives and offers to encourage the customers. The organizations are trying to defend the market share while achieving the maximum possible profit from the product.
04. Decline Stage
This is the last stage of the product life cycle which the demand for the product slowly goes downward. At this stage, the demand for the product gets decreased and the organization’s revenues go down. Once the organization reaches this level it has three options.
- Maintain the product with added features
- Reduce the product cost and supply the product to a selected small share of the market. (possible o the most loyal customer base)
- Discontinue the product and exit the market.
Marketing mix plays a major role in the product life cycle. It gives an opportunity for the managers of the organization to foresee the product status and create their strategic plans.