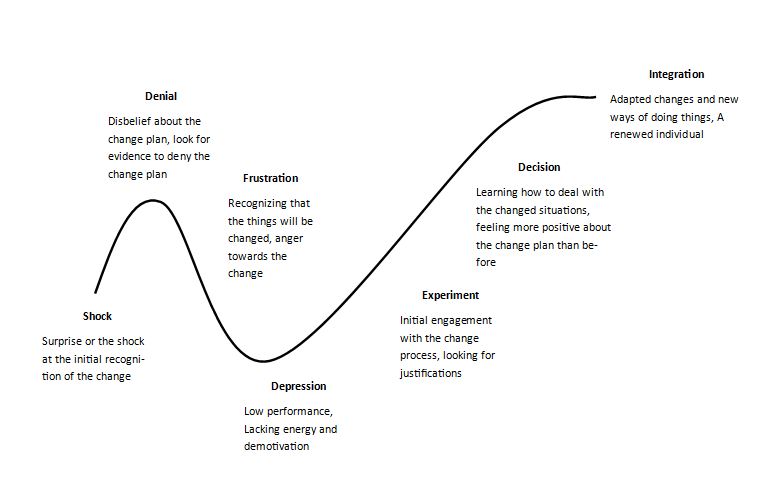
Change is one of the hardest processes any organization has to go through. Many change experts have introduced change management models to create a smooth change management process such as Kotter’s change management model, Lewin’s change management theory, and ADKAR change management model. Kubler-Ross change curve is another important change management model that explains the internal emotional journey that usually experiences by individuals when going through a change process in any organization.
The journey of a change is a combination of many emotions for any employer. At different stages of the change process, they continuously go through different types of emotions based on their experiences. The emotions can vary from shock and denial, anger, bargaining, depression, and acceptance. Based on this movement of emotions, Elizabeth Kubler-Ross has introduced the Kubler-Ross change curve which helps the change management teams all around the world.
The initial emotion of any employee, soon after they get to know about the change process can be identified as the shock of the feeling of change. Since people usually resist change, especially when it comes to a change that is necessary to move out from the comfort zone of the person, they tend to get shocked about the feeling of change.
Denial is another emotion that is combined with the initial shock feeling. It is an emotion of shock that can be identified with an added energy. Employees tend to deny the change by not supporting or encouraging the change process. This denial process reaches an intolerable level eventually creating an emotion of anger towards the change process. The idea of ‘unfairness’ in the change process majorly creates the emotion of anger. Anger can lead to blames and aggressive behavior towards the change management process.
According to the Kubler-Ross change curve, the continuation of anger emerges as a mood and turns to empathy towards self. This empathy makes the employee have a broader vision about the change process and its impact on the self is considered thoroughly. This will create the employees to understand the cost of the sacrifices they have to make personally towards a successful change process. This will lead to the emotion of bargaining where the employees try to emphasize the number of sacrifices they have to do in order to achieve the expected change.
Based on the explanation in the Kubler-Ross change curve, the bargaining emotion leads the employees to the emotion of depression. Once they understand that shock, anger, and bargaining emotions are not able to do any interruption to the change process, the emotion of depression kicks in creating the employee more nervous about the entire change process. This leaves the employees at their lowest performance. Correct leadership, empathy towards the employee feelings, active listening, solve employee issues through discussions can help employees in this situation.
To overcome these emotions, the next phase is the emotion of acceptance. Once the employees are realized that all the downward emotions are not helping them or for the change process, they tend to accept the change and adjust themselves for the new processes. In deeper levels, the employees identify that the change is happening no matter what their feelings about it are, and accept that it will be the future of their work, and starting to get used to the change. This is the stage where they are starting to explore the new possibilities in the new process and try to actually support the change management process.
According to the Kubler-Ross curve, after this point, the employee starts to engage in problem-solving behaviors. Employees actually engage in the change activities and look for new possibilities and opportunities that will allow them to understand and make the processes easy.
It is the responsibility of the change management team to identify that the employees are going through all these emotional changes when conducting a change program. They should always make sure to understand the employees, listen to them, and understand their concerns and support them to overcome the emotional drawbacks.