Market failure is the situation the free-market fails in efficient distribution of goods and services. It is believed that in a free market economy, allocative efficiency is achieved through a price mechanism. In a situation of market failure, the consumer can have the desired quantity of goods and services at the price they wish. If the price increases, the quantity demanded reduces, and the supply increases. More resources are allocated to produce the product in the short run and in the long run, more firms enter the market to receive excess profit. Thereby, the supply increases and the price falls creating market failure.
Free market functions on certain conditions such as free mobility of factors, rational behavior of consumers, availability of information about the market, unavailability of close substitutes, free entry and exit the market, large number of buyers and sellers, no government interference, etc. When these conditions are not met, the free market fails. Some of the situations where the free market fails can be identified as below.
- Government intervention
- Taxes and subsidies
- Price control
- Public and merit goods
- Presence of externalities
- Forming monopolies
- Asymmetrical information
- Immobility of factors of production
- Income distribution inequalities
Government intervention
- Taxes and subsidies
It is assumed that in a free market, theoretically, there is no government intervention in economic activities. But in almost all the countries, the governments exert their influence in different degrees to regulate the economy, when the market mechanism does not deliver the desired objectives.
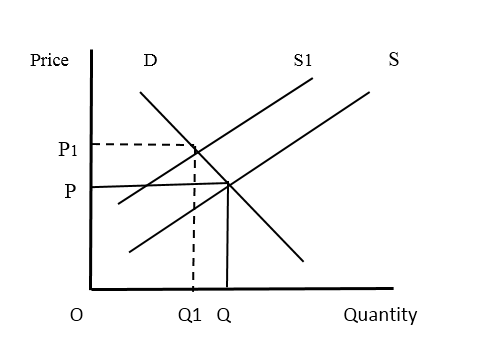
Imposing taxes is one of the mechanisms the governments use. The taxes are of two types, namely, direct taxes and indirect taxes. When a direct tax is imposed on a product, it cannot be shifted to the consumer by adding to the price of the price and the producer has to bear it. As a result, the cost of production increases, profit margin falls and as a result, the supply falls.
The decrease in supply increases the free market price. Imposing indirect taxes too directly affects the free market price. Indirect tax is initially paid by the producer and subsequently, burden is passed on to the consumer by adding it to the price of the product. As a result, the supply reduces and the price of the product increases.
Effects of Government taxes on free market
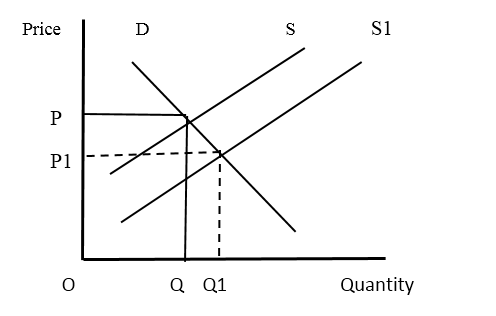
Provision of subsidies to the producers is another situation that the free market fails. If the producers of essential products to the economy find it difficult to cover up the production cost, the governments bear a part of the cost in the form of subsidies. It is an encouragement to the producers and as a result, the production will be increased by shifting the supply curve to the right. It is considered because the free market price does not exist.
Effects of Government subsidies
- Price control
There situations that the governments impose price ceiling (maximum price) or price floor (minimum price) on certain goods. If the free market price of an essential product which most of the consumers cannot buy it at that price, the government may fix a maximum price at which the product should be sold. Maximum price is always below the free market price.

As per the above diagram, the government has fixed a price ceiling as “P1” against the free market price “P”. Since it is a comparatively low price, it has created an excess demand of Q1 to Q2 units. It means that most of the consumers do not get the product. Due to the competition among the consumers, the price of the product tends to go up. The government has to fill the excess demand otherwise black market prices are inevitable.
Fixing a minimum price of setting a price floor will bring opposite results in the market. The price floor should always be above the free market price. This is a measure taken by the governments to protect the products of essential nature. Once the minimum price is fixed, the producers can sell the product at that price. The market effects of a price floor can be observed by using a diagram as below.
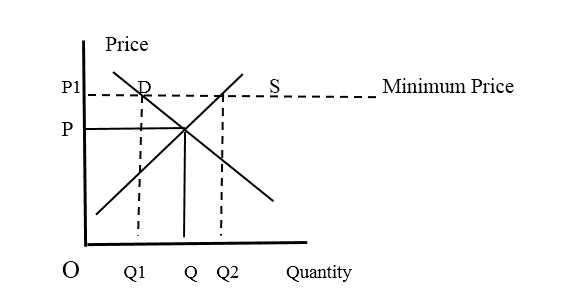
Minimum price has fixed ad “P1” above the free market price “P” by the government. As a result the supply of the product has increased and Q1 to Q2 amount of excess supply has been created. Excess supply generates a competition among the producers and the price tends down unless the government takes some measures to eliminate the excess supply from the market.
- Provision of public and merit goods.
Public goods are the product that cannot be provided through the free market because of their following characteristics.
- Price cannot be fixed because there is no opportunity cost of providing it to another.
- Non- rivalry
- Non-excludability
In addition, merit goods are the goods that the government considers that everyone should have, eg. Education, Health facilities, etc. these are partly provided by the government as well as the private sector through the free-market mechanism.
Presence of Externalities
Externalities are the effects of either consumption or the production to the society which is not reflected in the personal accounts. Externalities are of two types.
- Positive externalities
These are the benefits or additional advantages either of consumption or production to the third parties. For example, an increase in land value in an area due to the location of an industry.
- Negative externalities – these are the negative effects or the disadvantages of either consumption or production to the external society. For example, damage caused by constructing a factory in an area.
The free market price does not reflect social cost or the benefit through the free-market mechanism. When determining the cost or the benefit only the private cost and the benefit are considered. Therefore, when externalities are present, the free market fails.
Forming Monopolies
In practice, more market power still exists with the imperfectly competitive market where monopolies and oligopolies are dominating over the free market. A monopoly is a market structure where more of the market power lies with only one or a few firms.
They have the ability to act as price makers in the market by controlling the amount supplied to the market, imposing entry barriers to new firms to the industries, advertising, or other rivalry measures such as introducing penetrating prices. Firms in imperfect competition fix the price above the marginal cost and enjoy abnormal profits against the free market. The free market price is determined by the market forces at the point where Marginal cost equals marginal revenue.
Abnormal profits of Monopoly

As per the above diagram, the price of the product is higher than the Marginal Revenue equals Marginal Cost (MR=MC). There is no efficient distribution of goods and services. Hence, the free market fails.
Other factors
Asymmetrical information, immobility of factors of production, the existence of income distribution inequalities are some other factors that lead to the failure of the free market. If the consumers, as well as the firms in the industry, are lacking market information, the free market fails. For example, the suppliers can sell the product at higher prices or may not be aware of the better opportunities of using available resources.
Factor immobility is another which leads to free-market failure. In practice, most of the factors are not freely mobile from one product to another. It involves an additional cost. Apart from that, income distribution inequality is high, the people do not get equal opportunities to accumulate wealth or consumption. Therefore, practically there are many factors that disturb the free market to failure.

