Trade barriers have become one major reason that slows down economic growth. Almost all the countries in the world involve in international trade in different degrees. Goods are imported and exported due to different reasons and trade is interconnected. In international trade, there are different restrictions of which some are natural and the others are imposed by respective countries. The reasons for imposing trade barriers are;
- Protect domestic industries from foreign competition
- Save foreign exchange
- Increase employment
- Protect consumers
- Preventing or eliminating balance of payment deficit
Trade barriers can be categorized as below.
- Natural barriers
- Tariff barriers
- Non-tariff barriers
Natural Barriers
Natural barriers are of two types, namely physical barriers and cultural barriers.
Distance is one of the natural barriers. The countries in trade are normally located far from each other. For example, the USA and Japan. When transporting goods between faraway countries, the transport cost is too high. Sometimes it may exceed the cost of production.
Language is another cultural barrier to international trade. Different countries use different languages and it poses a communication issue in trade. Though English is used as an international language, there are situations in which the people are not much familiar. Apart from that, there are situations that the goods are not traded due to religious reasons too.
The chart below shows different types of trade barriers in existence.
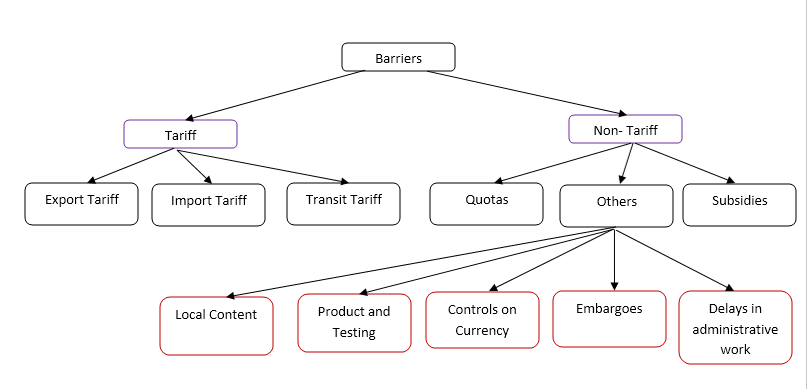
Tariff Barriers
A tariff is a tax imposed by the government at the time importing goods. The value of the tax is initially paid by the importer and subsequently added to the price of the product. The tariff is imposed in two different ways.
- Per-unit tariffs – tax is levied based on the number of units imported.
- Ad valorem or Percentage tariff – tariff is imposed on the value of the goods imported
A tariff is a tax in which the incidence can be shifted to the final consumer. After paying the tariff, the importer subsequently adds it to the price of the product. The price of the product increases in the domestic market and as a result, the demand for imports falls. Thereby the government can restrict the imports of all the goods or of some selected products. At the same time, it gains an income to the government and reduces the competitiveness in the domestic market providing an incentive to the domestic industries. The market effects of tariffs can be observed by using the following diagram.
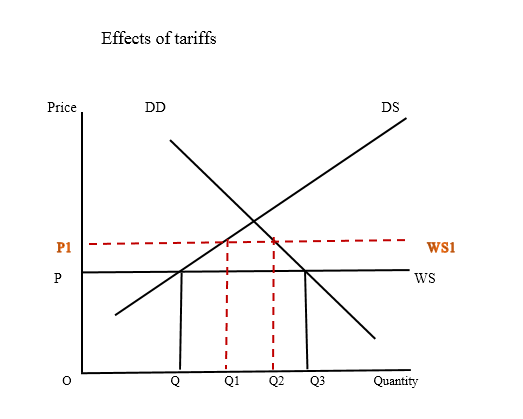
As per the diagram, before the tariff, the O – Q3 amount of the product is demanded of which O – Q amount is supplied by the domestic producers. The remaining Q – Q3 amount is imported. The situation changes due to the tax by increasing the price of the product from P to P1. An increase in price reduces the demand from Q3 to Q2 and the domestic supply increases from Q to Q1. The impact of the tariff is reducing the amount imported from Q, Q3 to Q1, Q2, as expected by the government.
Quotas
Quota is a physical limitation of imports to the country for a given period of time. Once the quota is imposed, the imports are restricted but it does not bring any revenue to the government.
market effects of imposing quota can be observed as below.
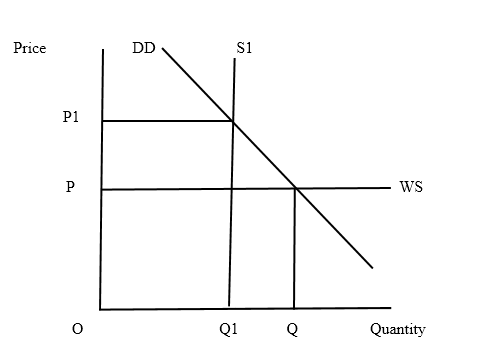
Before the quota is imposed, the imports account for Q1 – Q2 amount and due to the quota, the amount imported has come down from Q to Q1. As a result, the domestic market price of the product has increased from P to P1.
Other trade barriers
Embargoes, Foreign currency restrictions, Voluntary Export Restrictions, product and testing, Administrative delays, etc. are some of the non-tariff trade barriers used by different countries based on different reasons. The embargo is a measure of totally banning the import of goods from a country. This can be imposed on all the goods imported from a country or a ban on a particular product.
Foreign currency control refers to imposing certain restrictions when allocating foreign currency needed for imports. Higher restrictions may discourage the importers and reduces the number of imports. In addition, the process of importing can be made more complicated that the importers are discouraged to follow.

